Ever wished you could have the latest version of Mozilla Firefox? Think no more. You actually can have it. Keep reading and you'll see how.
On the date of this post the latest version of Firefox that I'm running is the one shown on the following picture (I'm downloading right now the 20080507 nightly build):
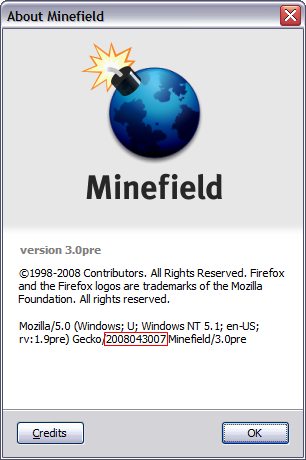
As you can see my current version is the one from April, 30th. Look inside the red rectangle. I don't download the nightly build everyday.
One thing interesting is the name: Minefield. Believe me: It's not that minefield as the name states.
Nightly builds
This is what the folks from the Mozilla developer division say about the nightly builds:
Nightly builds are created most weekdays from the previous day's work, these builds may or may not work. Use them to verify that a bug you're tracking has been fixed.
We make nightly builds for testing only. We write code and post the results right away so people like you can join our testing process and report bugs. You will find bugs, and lots of them. Mozilla might crash on startup. It might delete all your files and cause your computer to burst into flames. Don't bother downloading nightly builds if you're unwilling to put up with problems.
I've been using the nightly builds for a long time and from what I found you can have the latest innovations in browsing technologies without worrying about lots of bugs or crashes. Using a nightly build is perfect. You can use it for your day to day navigation. It's really stable. From what I remember it has crashed 2 or 3 times in a time span of more than 1 year. Besides that, no worries!
Firefox features I like most
From the innovations and my own tweaks, the ones that I like most are:
- URL auto-completion
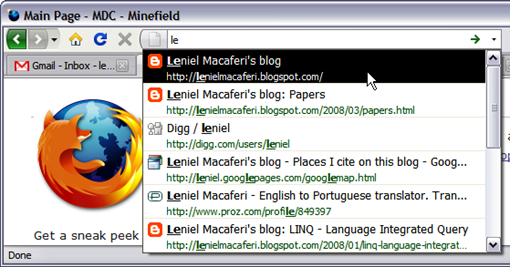
One of the greatest features (there are lots of them) is URL auto-completing - they call it "Location bar and auto-complete". Type the title or tag of a page in the location bar to quickly find the site you were looking for in your history and bookmarks. Favicons, bookmark, and tag indicators help you see where the results are coming from.
This is implemented through a lightweight database that stores the URLs already visited. The more you access a URL the high will be its rank in the list of visited URLs. You just start typing the address and instantly you get the URL you're after. You don't need to type the whole thing every time. It's a must. I use it all the time. See it in action:
- New revamped Download Manager
The Download Manager is fantastic too. You don't need to start your downloads all over again in case you interrupt them. You can resume from the point you stopped. You can check more info about its improvements in the next version of Firefox at the page Download Manager improvements in Firefox 3. See its face:

- More available screen size (this is my own tweak)
More size to see the web page content. You can personalize your browser so that your toolbar buttons don't fill the space you could use to visualize content and more content. Check how I customize my browser so that I have the best fit:

I've shrunk the above window to show it here, but you have a big space to type your URLs in the location/address bar.
I don't have any toolbar. I just put all the buttons I use most on the left of the address bar and the standard menus on the right. To do this simply right-click on one of the menus and select "Customize...". From there you can change the disposition of the buttons. Click and hold one of the buttons and put it anywhere you want. As I did I put them on the left and right side of the address bar. I just don't use the standard toolbars that are: the Navigation toolbar and the Bookmarks toolbar. To not use them, uncheck them. What you gain? More space.
- Restore Previous Session
Restore Previous Session is the other one that I think is really helpful. You see, while I was composing this post I had to get some screenshots. To do this I should have pressed the key Print Screen on the keyboard but instead I pressed the key Power that is just above the Print Screen one. What happened? My computer hibernated. I did this for three times in a row. The last one I hit the restart button on my machine while it was going to hibernate. I don't know why I did it. I lost all the applications that were in memory. Firefox was one of them. Now I just came back to continue typing this post and opened Firefox again. What did I get? The following dialog:
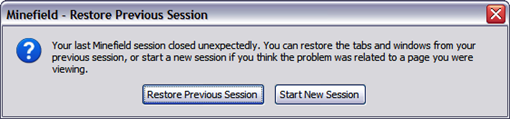
Clicking on Restore Previous Session, Firefox brought back all the tabs that were open the time the computer was turned off accidentally. Fantastic, isn't it? It can help a lot in case of power failure too.
The change from Internet Explorer to Firefox
I remember that I was reluctant in changing from Internet Explorer to Firefox. I decided to try Firefox one day. I installed and used it a little bit and I didn't like it, so I uninstalled and continued using Internet Explorer. I don't remember exactly when I gave it a second chance, but the fact is that I gave and this time I think it is forever. After playing with it a little bit more I saw how customizable it was through add-ons, etc (e.g.: the tweak I did with the toolbars isn't possible with Internet Explorer).
After the changing I don't want to go back to IE. Firefox is much superior in quality and velocity. You navigate the internet really faster.
Remember one thing though: you should have a version of Internet Explorer in case you need it for a site that doesn't work well with Firefox. Yes, there are sites and forms that don't play well with Firefox yet. If you ever be in such a situation, just open IE and try with it. That's what I do and it has worked fine.
How to get Firefox
If you don't know, Firefox runs on various versions of Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and many other Unix-like operating systems.
You have three options and on the date of this post the Firefox versions you can download are:
The current stable release version
Firefox 2.0.0.14. You can get it at the page Firefox web browser | International versions: Get Firefox in your language.
Beta version
The beta version is Firefox 3 beta 5. You can get it at the page Firefox web browser (beta) | International versions: Get Firefox in your language.
Nightly builds
Nightly builds are the ones I use. Each day we have a new one. You can get it at the latest trunk page.
Final notes
It's impossible to comment on every part of Firefox that I like. I hope that you could have gotten the notion of a few of the capabilities of this splendid piece of software. I think of Firefox as a work of art. In truth it's what it is: a work of art.
Firefox's source code is free software.
The open source community must be recognized as a powerful and expressive one. They are on the scene. Congratulations to everyone that helps make Firefox such an work of art. It's amazing to realize how a collaborative work has evolved impressively during the last years.
Folks, keep up the great job and continue innovating all the time. That's what makes someone like me write a post like this.
References
Mozilla Firefox article at Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mozilla_Firefox
The History of Mozilla Firefox article at Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Mozilla_Firefox
mozilla - Developer Central
http://www.mozilla.org/developer/
Complete list of Firefox 2.0.0.14 features
http://www.mozilla.com/en-US/firefox/features.html
Recommended Add-ons :: Firefox Add-ons
https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/recommended
Firefox 3 for Developers - Mozilla Developer Center (MDC)
http://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Firefox_3_for_developers





