To close this series of posts, today I’m going to match some input strings using the regex (l|e)*n?(i|e)el* that we’ve been using since the beginning.
To match the strings I’ll make use of the DFA we constructed in the last post titled Regex engine in C# - the DFA.
These are the 20 strings I’ll be matching:
eee, eeeil, eel, ennil, ie, leie, lele, leleel, lelel, lelenil, leliel, leniel, llnel, ln, lnel, lniel, nelll, niel, nil and nll.
In the DFA class we have a method called Simulate which I show bellow:
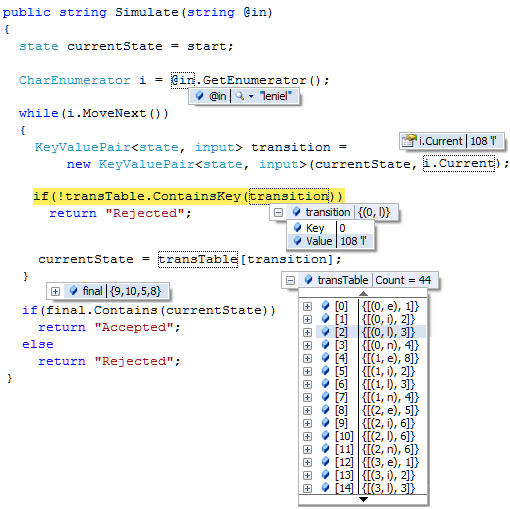
public string Simulate(string @in) { state currentState = start; CharEnumerator i = @in.GetEnumerator(); while(i.MoveNext()) { KeyValuePair<state, input> transition = new KeyValuePair<state, input>(currentState, i.Current); if(!transTable.ContainsKey(transition)) return "Rejected"; currentState = transTable[transition]; } if(final.Contains(currentState)) return "Accepted"; else return "Rejected"; }
The Simulate method takes as input a string to be matched and returns a string that signalizes success or failing when matching such a string.
To test it I’ll match the string “leniel” which by the way is my own name. :-)
So, what the Simulate method do?
It starts by assigning the start state 0 to the variable currentState.
Next we get a charEnumerator that is used in the while block to move letter by letter (input symbol by input symbol) till we get to the end of the string.
We declare a KeyValuePair<state, input> designated transition that has as the key the currentState and as the value the current input symbol we’re simulating.
We check to see if the DFA’s transition table contains such a transition, that is, if there’s a valid path from that state with that input symbol to another state. If it doesn’t, we reject the string we’re matching, otherwise we make the currentState variable receive the next state, that is, the state appointed by the transition we’ve just checked.
The process inside the while block goes on until we reach the last input symbol taken from the string we’re matching, in this case, the last “l” letter.
After getting out of the while block we make a final check to see if the state we achieved is part of the DFA’s set of final states. If it is, we accept the string, otherwise, we reject it.
This is an x-ray from the variables’ value when in the first iteration of the while block:
As you can see in the transition table, from start state (currentState) “0” with the fist input symbol “l” we can go to state “3”.
The following table shows the result obtained while testing the strings mentioned above:
| Accepted | Rejected |
|---|---|
|
eee |
eeeil |
|
eel |
ennil |
|
ie |
lele |
|
leie |
lelel |
|
leleel |
lelenil |
|
leliel |
llnel |
|
leniel |
ln |
|
lniel |
lnel |
|
niel |
nelll |
|
nil |
|
|
nll |
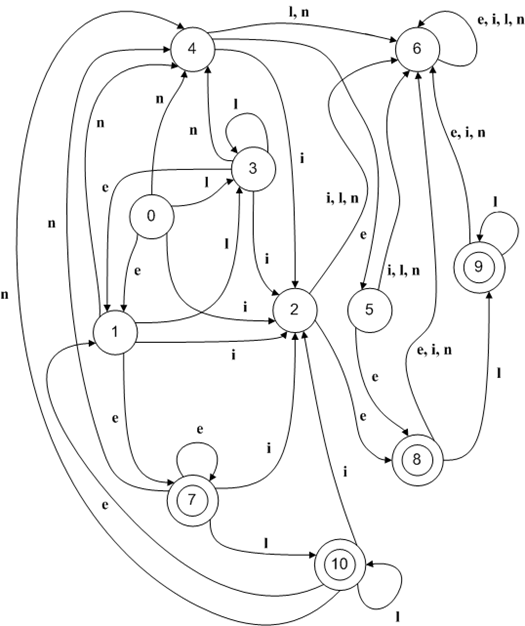
To make sure it’s correct, debug each one of these strings visually looking at the DFA’s graph representation shown below. Starting at state 0 we must end in one of the final states {7, 8, 9, 10}.
The Regex Engine executable
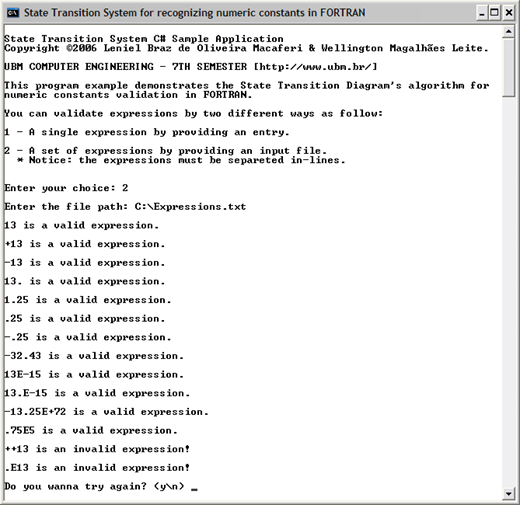
The Regex Engine presented in this series of posts is a C# Console Application. As such it was written in a way that its command line arguments must be entered in the following form:
RegularExpressionEngine "(l|e)*n?(i|e)el*" leniel
Where:
RegularExpressionEngine -> the name of the executable .exe file (the program itself)
"(l|e)*n?(i|e)el*" –> between the double quotes we pass the regex
leniel –> the string we want to match in the regex
Using Microsoft Visual Studio C# 2008 we can set the command line arguments using the Debug properties page of the project like the following picture:

To get to the Debug page, right click in the solution inside Solution Explorer as shown in the following picture:

After setting the command line arguments, hit F5 and you’re ready to go.
The Regex Engine source code
You can get the complete code (Microsoft Visual C# 2008 Console application) and executable at:
http://leniel.googlepages.com/RegularExpressionEngine.rar
To try out the code you can use the free Microsoft Visual C# 2008 Express Edition that you can get at: http://www.microsoft.com/express/vcsharp
Updated on 5/12/2009 10:06:00 PM
As I finished writing the posts, here goes the list that points to them:
Regular Expression Engine in C# (the Story)
Regex engine in C# - the Regex Parser
Regex engine in C# - the NFA
Regex engine in C# - the DFA
Source code: https://github.com/leniel/RegexEngine
References
The following links can help you when dealing with regexes:
Regular-Expressions.info - Regex Tutorial, Examples and Reference - Regex Patterns
http://www.regular-expressions.info
Regular Expression Library (great site with lots of regexes and an excellent regex tester)
http://regexlib.com/Default.aspx
http://regexlib.com/RETester.aspx